Qt Signal Slot Cross Thread
Qt provides several ways to implement Inter-Process Communication (IPC) in Qt applications.
TCP/IP
The cross-platform Qt Network module provides classes that make network programming portable and easy. It offers high-level classes (e.g. QNetworkAccessManager) that communicate using specific application-level protocols, and lower-level classes (e.g., QTcpSocket, QTcpServer, QSslSocket) for implementing protocols.
Local Server/Socket
- It may be stored inside the signal like in wigwag and boost, or inside the base class like in Qt and, probably, GObject. So, if noone connected to a signal, you still have that overhead of an empty handlers list with any approach. Regarding sharing a single mutex between signals, boonsoftware is right: it is quite easy to do that in wigwag.
- The QThread::run method only spins (exec in Qt parlance) an event loop (of course it won't do it anymore if your reimplementation doesn't). An event loop waits for events to arrive in the queue, and then notifies the target QObjects of their reception. The cross-thread (queued) signal-slot connections are implemented by leveraging events.
The cross-platform Qt Network module provides classes that make local network programming portable and easy. It offers the QLocalServer and QLocalSocket classes that allow for network-like communication in a local setup. Their TCP counterparts can be used as drop-in replacement to make the communication work across networks.
Shared Memory
The cross-platform shared memory class, QSharedMemory, provides access to the operating system's shared memory implementation. It allows safe access to shared memory segments by multiple threads and processes. Additionally, QSystemSemaphore can be used to control access to resources shared by the system, as well as to communicate between processes.
Signals and slots are used for communication between objects. The signals and slots mechanism is a central feature of Qt and probably the part that differs most from the features provided by other frameworks. Signals and slots are made possible by Qt's meta-object system.
D-Bus protocol
Qt Signal Slot Cross Thread Gages
The Qt D-Bus module is a Unix-only library you can use to implement IPC using the D-Bus protocol. It extends Qt's Signals and Slots mechanism to the IPC level, allowing a signal emitted by one process to be connected to a slot in another process. The Qt D-Bus documentation has detailed information on how to use the Qt D-Bus module.
QProcess Class
The cross-platform class QProcess can be used to start external programs as child processes, and to communicate with them. It provides an API for monitoring and controlling the state of the child process. QProcess gives access to the input/output channels of child process by inheriting from QIODevice.
Session Management
Qt Signal Slot Not Working
On Linux/X11, Windows and macOS, Qt provides support for session management. Sessions allow events to be propagated to processes, for example, to notify when a shutdown occurs. The process and applications can then perform any necessary operations such as save open documents.
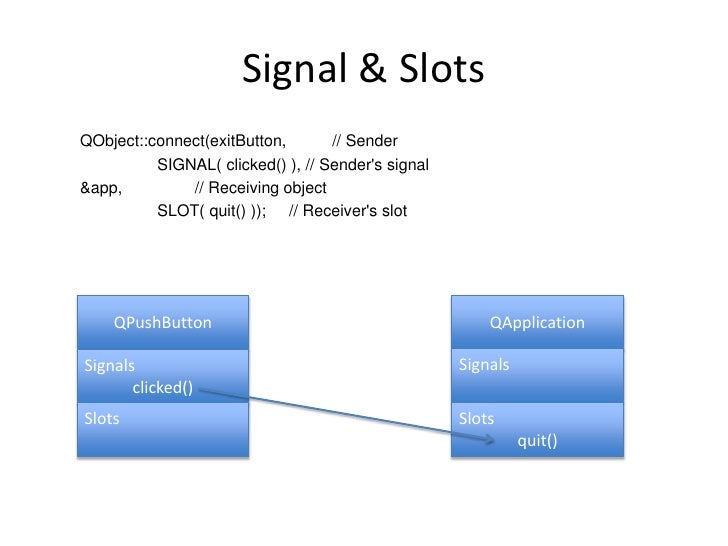

Qt Signal Slot
© 2020 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.